publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2023
- JMI
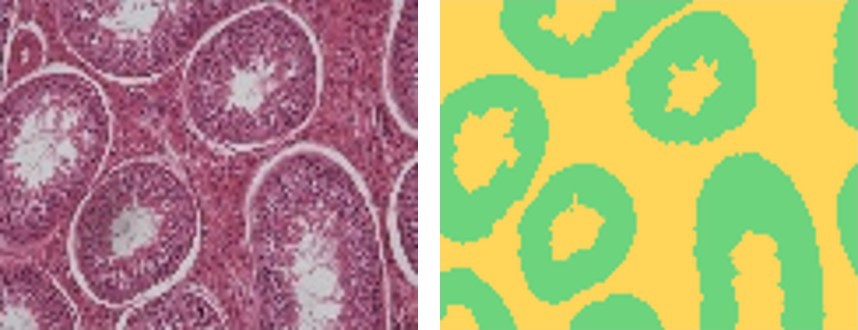 Deep learning-based method for segmenting epithelial layer of tubules in histopathological images of testicular tissueAzadeh Fakhrzadeh, Pouya Karimian, Mahsa Meyari, and 5 more authorsJournal of Medical Imaging, 2023
Deep learning-based method for segmenting epithelial layer of tubules in histopathological images of testicular tissueAzadeh Fakhrzadeh, Pouya Karimian, Mahsa Meyari, and 5 more authorsJournal of Medical Imaging, 2023There is growing concern that male reproduction is affected by environmental chemicals. One way to determine the adverse effect of environmental pollutants is to use wild animals as monitors and evaluate testicular toxicity using histopathology. Automated methods are necessary tools in the quantitative assessment of histopathology to overcome the subjectivity of manual evaluation and accelerate the process. We propose an automated method to process histology images of testicular tissue. Segmenting the epithelial layer of the seminiferous tubule is a prerequisite for developing automated methods to detect abnormalities in tissue. We suggest an encoder-decoder fully connected convolutional neural network (F-CNN) model to segment the epithelial layer of the seminiferous tubules in histological images. Using ResNet-34 modules in the encoder adds a shortcut mechanism to avoid the gradient vanishing and accelerate the network convergence. The squeeze & excitation (SE) attention block is integrated into the encoding module improving the segmentation and localization of epithelium. We applied the proposed method for the 2-class problem where the epithelial layer of the tubule is the target class. The f-score and IoU of the proposed method are 0.85 and 0.92. Although the proposed method is trained on a limited training set, it performs well on an independent dataset and outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. The pretrained ResNet-34 in the encoder and attention block suggested in the decoder result in better segmentation and generalization. The proposed method can be applied to testicular tissue images from any mammalian species and can be used as the first part of a fully automated testicular tissue processing pipeline. The dataset and codes are publicly available on GitHub.
@article{10.1117/1.JMI.10.3.037501, author = {Fakhrzadeh, Azadeh and Karimian, Pouya and Meyari, Mahsa and Hendriks, Cris L. Luengo and Holm, Lena and Sonne, Christian and Dietz, Rune and Sp{\"o}rndly-Nees, Ellinor}, title = {{Deep learning-based method for segmenting epithelial layer of tubules in histopathological images of testicular tissue}}, volume = {10}, journal = {Journal of Medical Imaging}, number = {3}, publisher = {SPIE}, pages = {037501}, keywords = {segmentation, deep learning, histological image, seminiferous tubules, Image segmentation, Tissues, Education and training, Data modeling, RGB color model, Histopathology, Convolution, Cross validation, Deep learning, Network architectures}, year = {2023}, doi = {10.1117/1.JMI.10.3.037501}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.10.3.037501}, }
2021
- M.Sc. Thesis
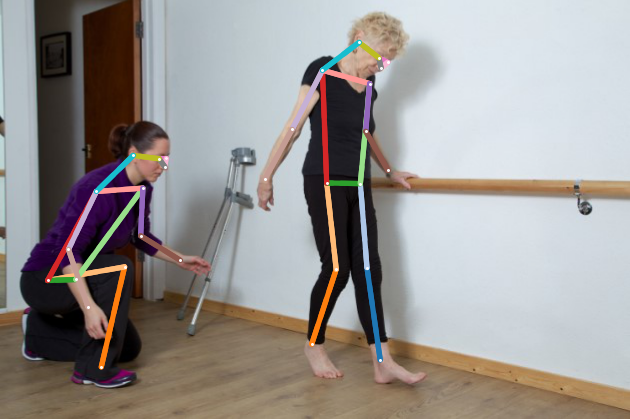 Human pose estimation for elderly carePouya KarimianIndustrial engineering department, Amirkabir university of technology, 2021
Human pose estimation for elderly carePouya KarimianIndustrial engineering department, Amirkabir university of technology, 2021As life expectancy increases in the world, the number of elderly people will increase in the coming years. With the increase in the number of elderly people and the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic, hospitals will no longer have the capacity to care for elderly patients for a long time and will inevitably have to turn to home health care. One of home health care items is to check and monitor physical activities such as physiotherapy exercises. Human pose estimation models in the field of computer vision can solve this problem well. In this study, a new 2D multi-person pose estimation model is introduced that can be used in elderly care. This bottom-up model includes a backbone network called Res2net to extract features and composite fields to estimate key points and connections. Our experiments demonstrated that the proposed model outperforms previous similar models in both performance and reliability in low resolution. Proposed model has suitable speed for real-time operation too and qualitative results showed that it is a practical model for elderly care.
2018
- B.Sc. ThesisSimulation of dosage and frequency of Aspirin intake based on Markov chainPouya Karimian2018